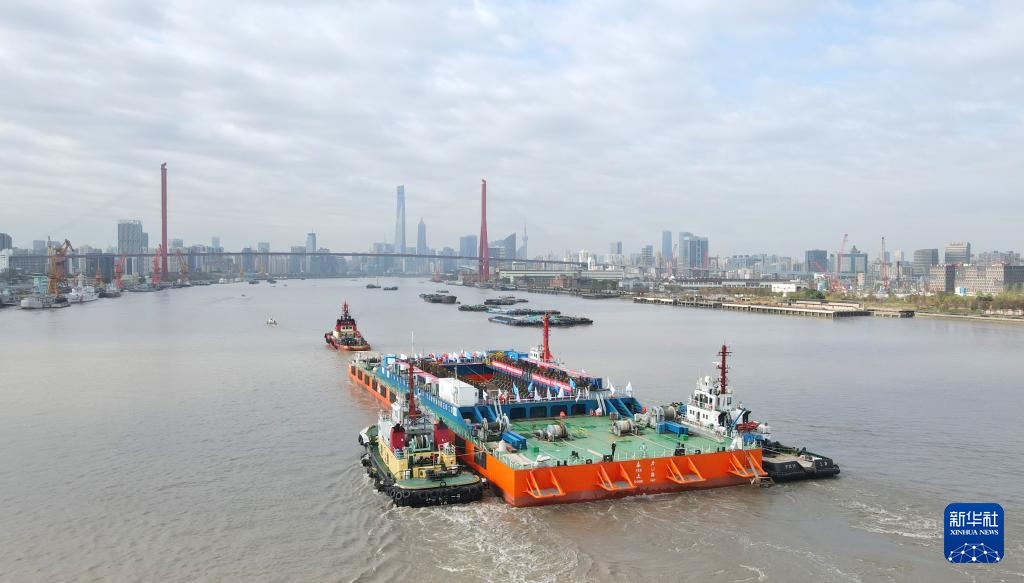

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)
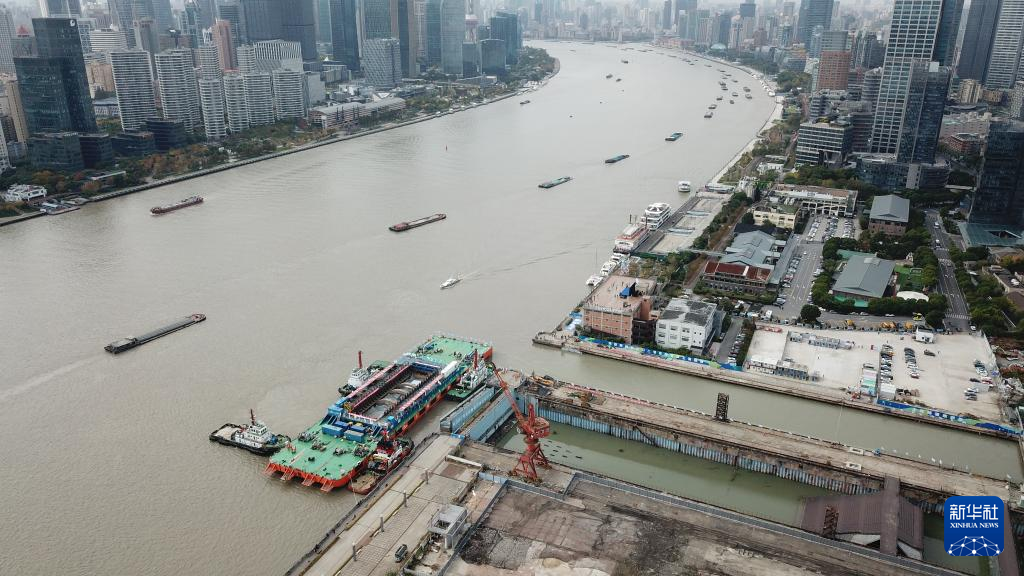

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
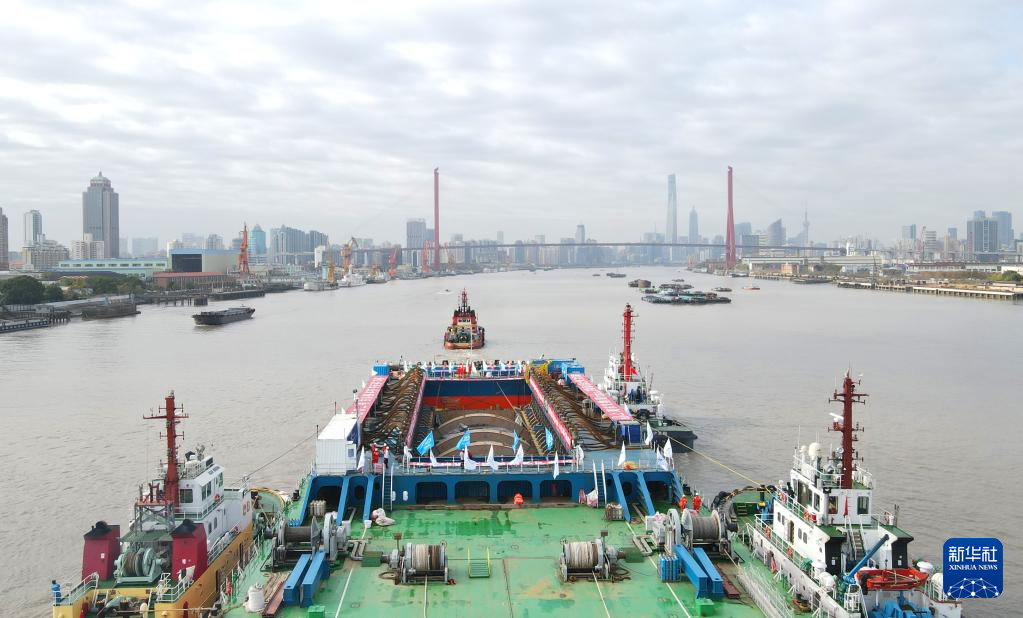

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)
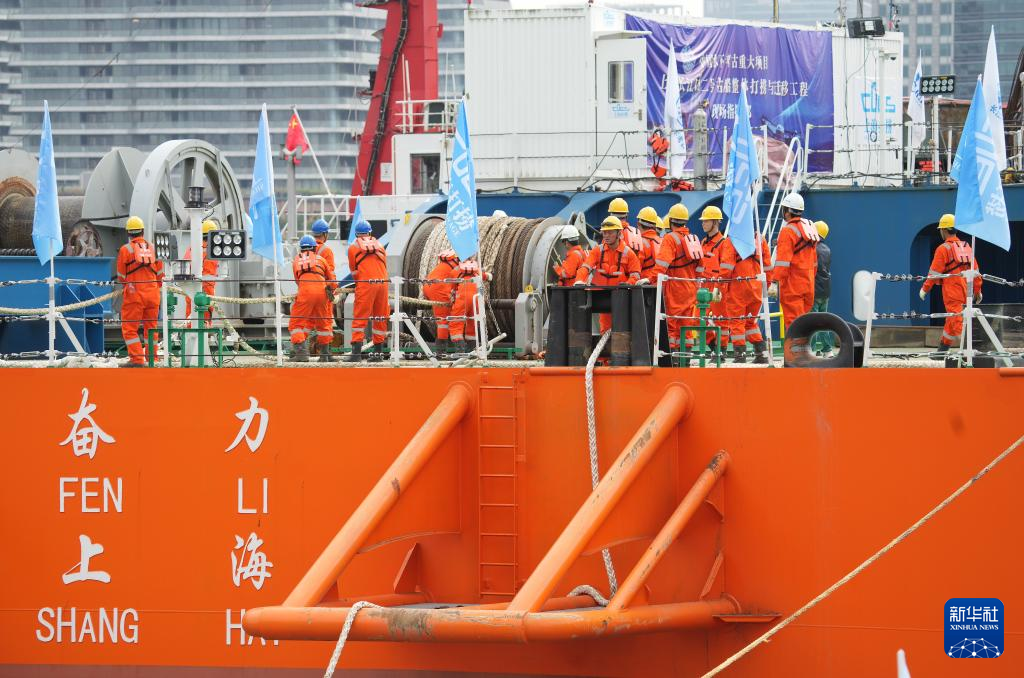

Staff members work as the Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Ding Ting)
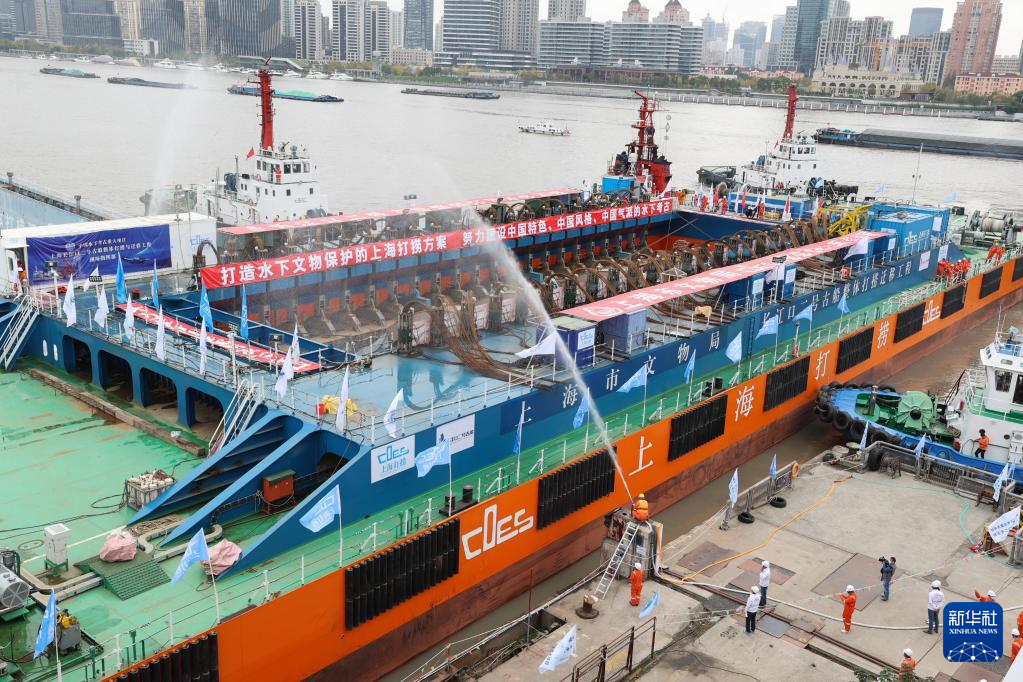

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
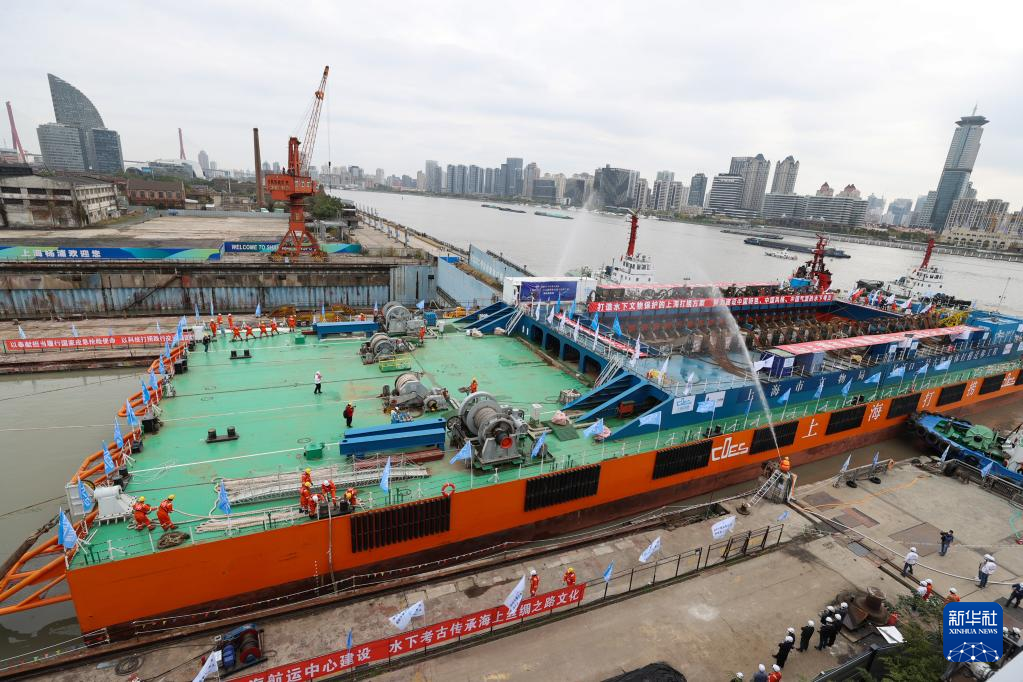

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
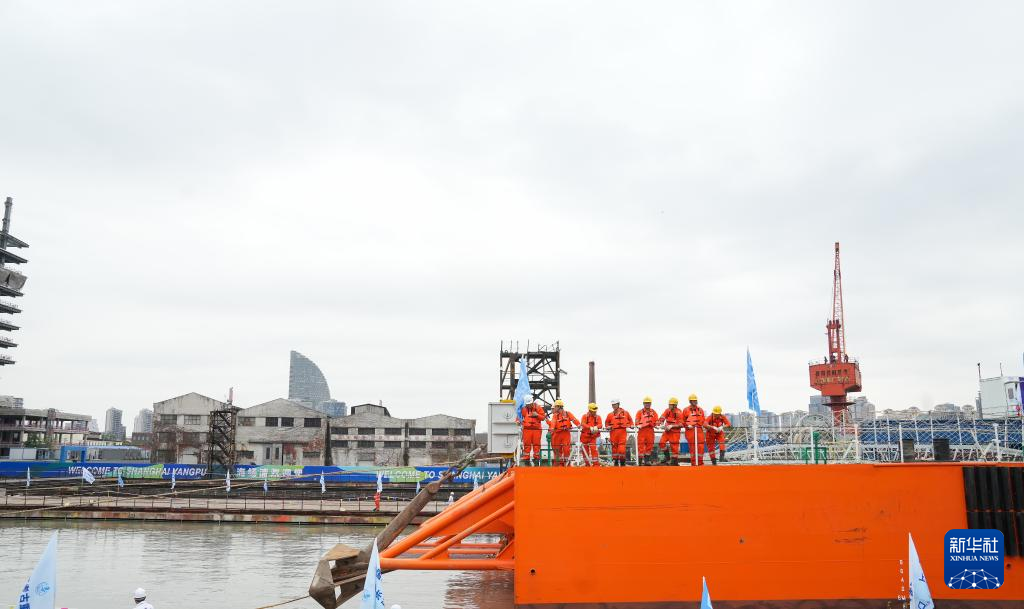

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Ding Ting)
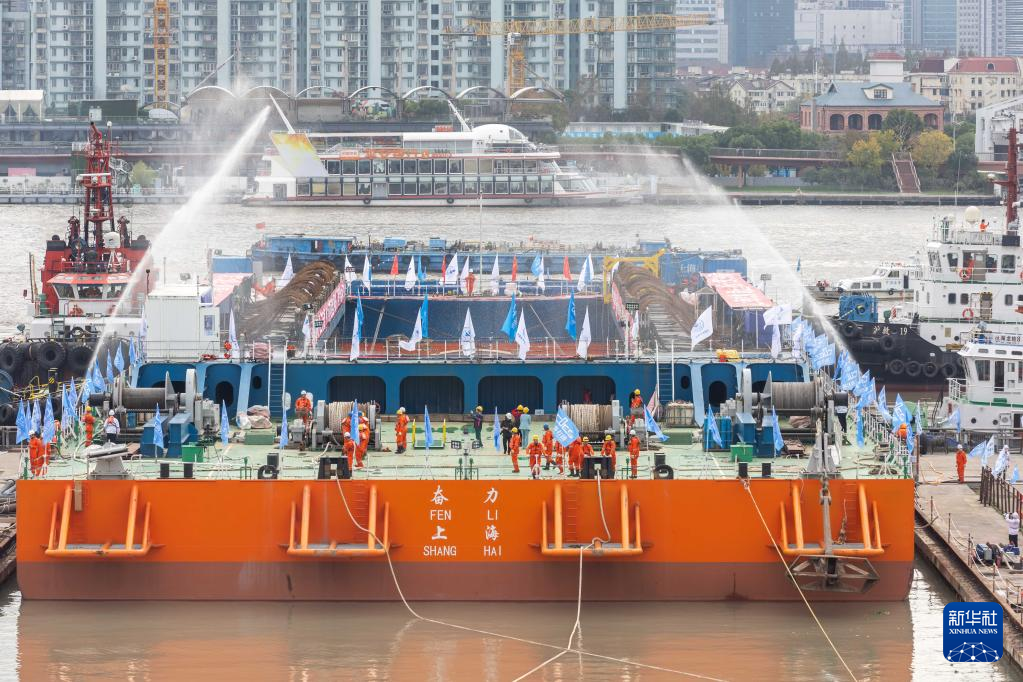

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Wang Xiang)
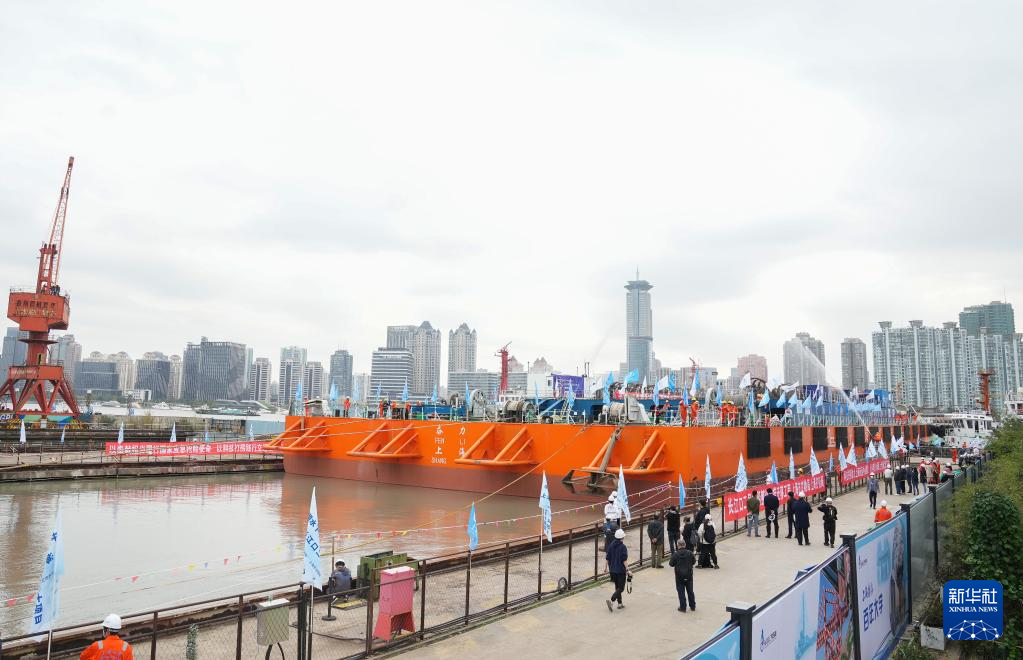

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Ding Ting)
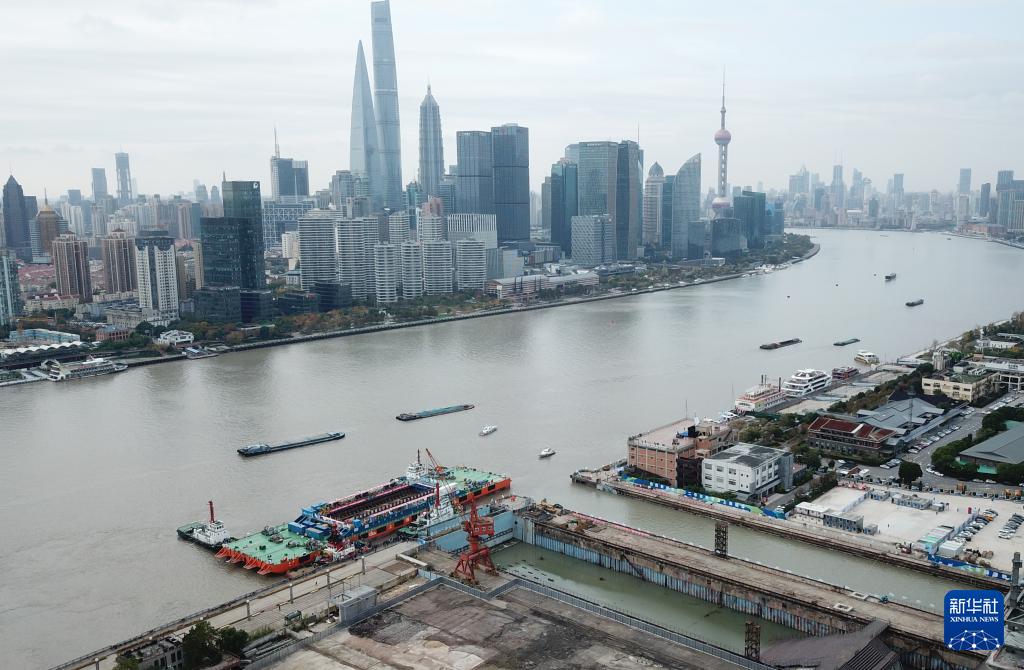

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
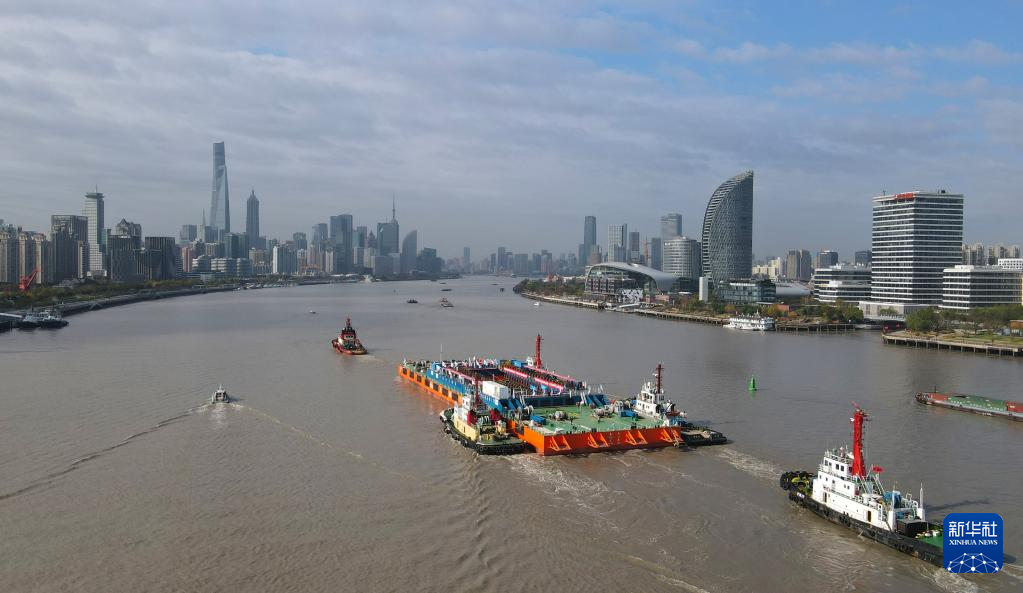

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)
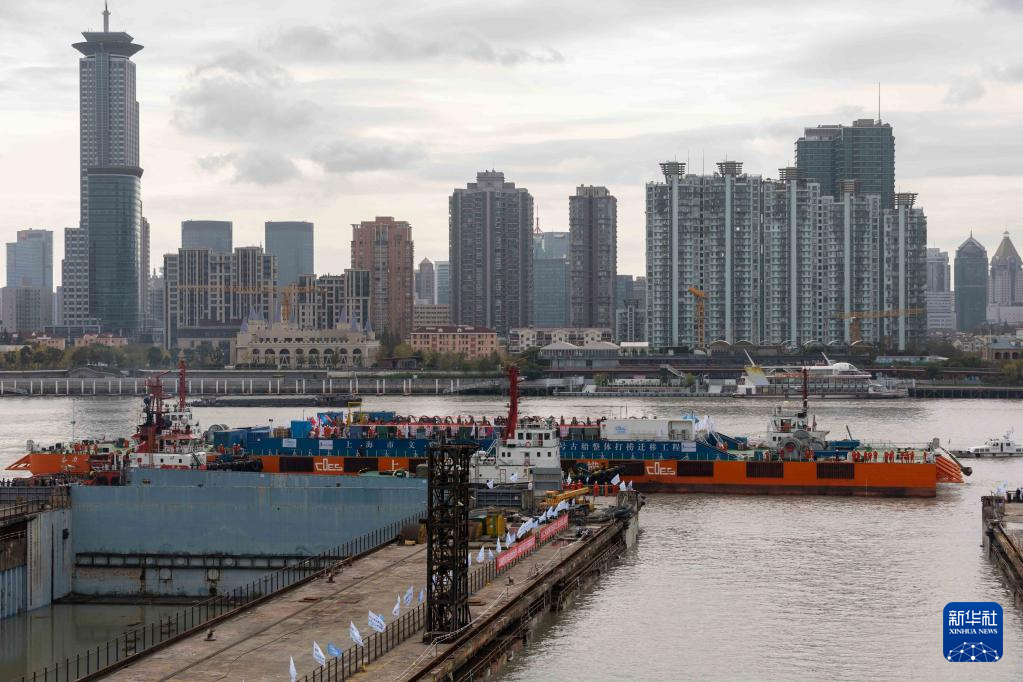

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Wang Xiang)
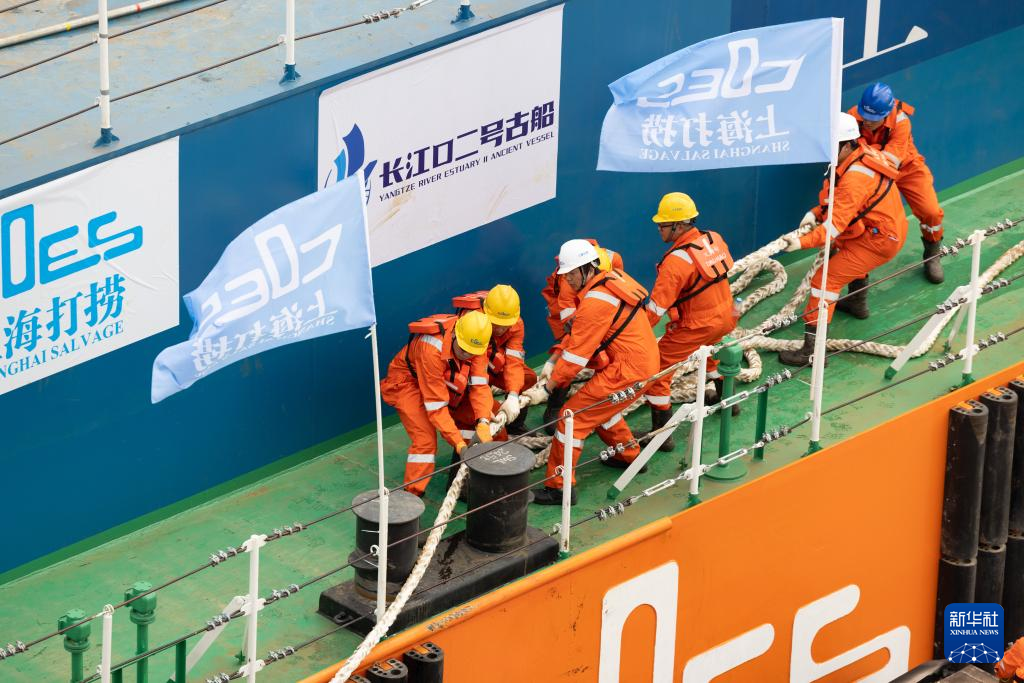

Staff members work as the Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
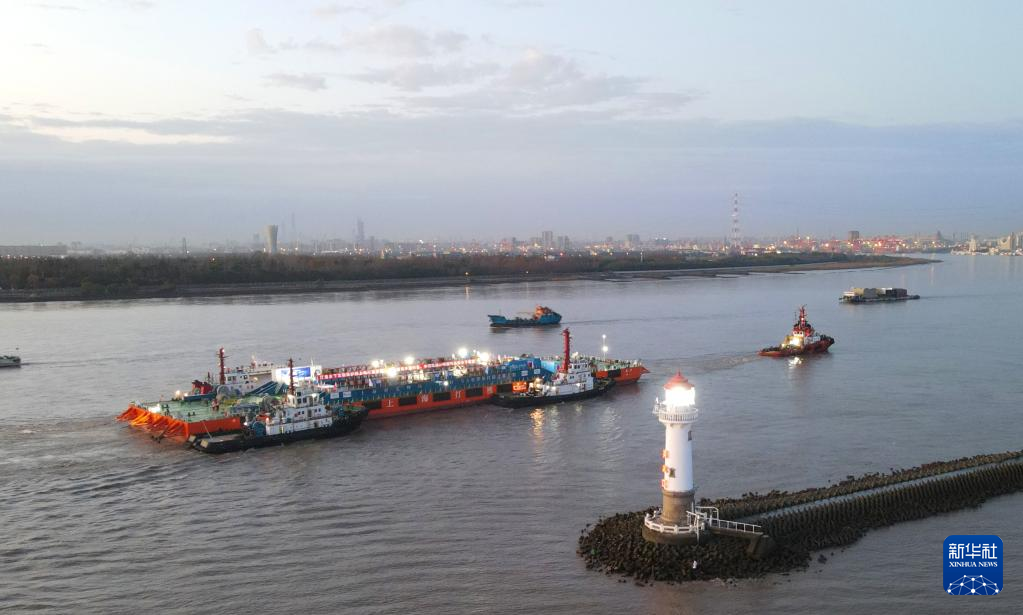

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)
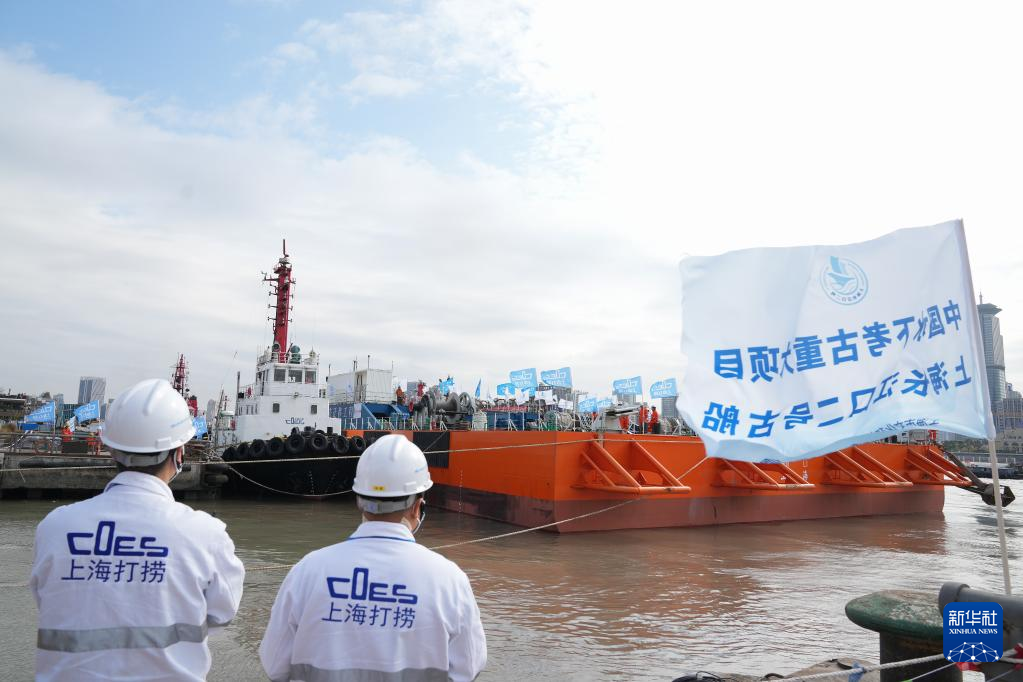

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Ding Ting)
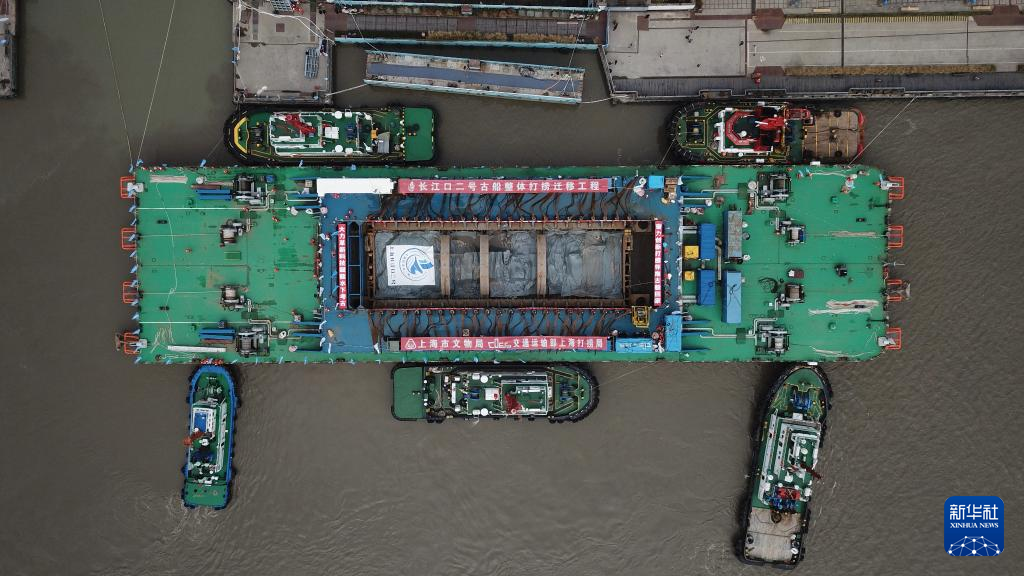

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
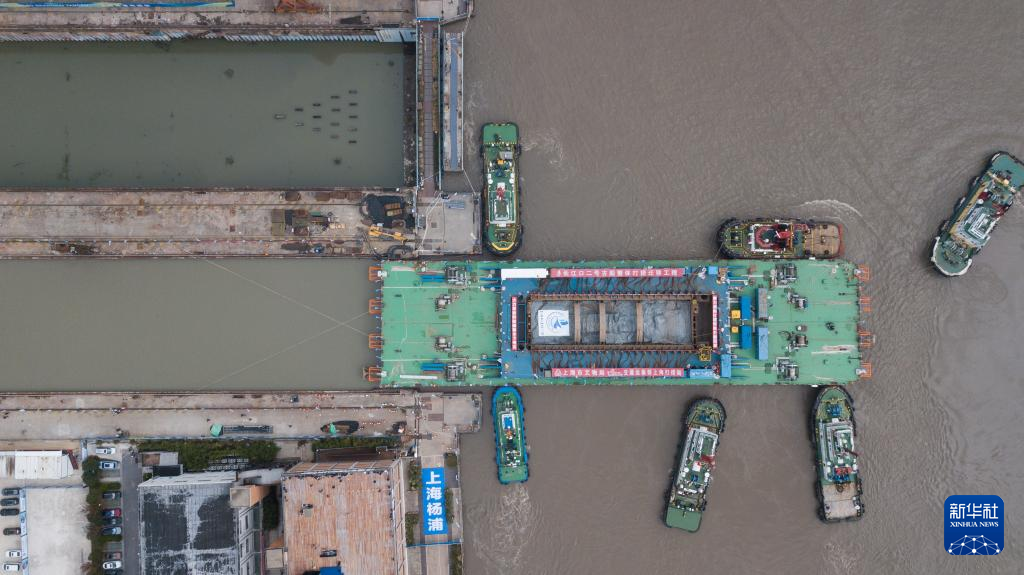

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
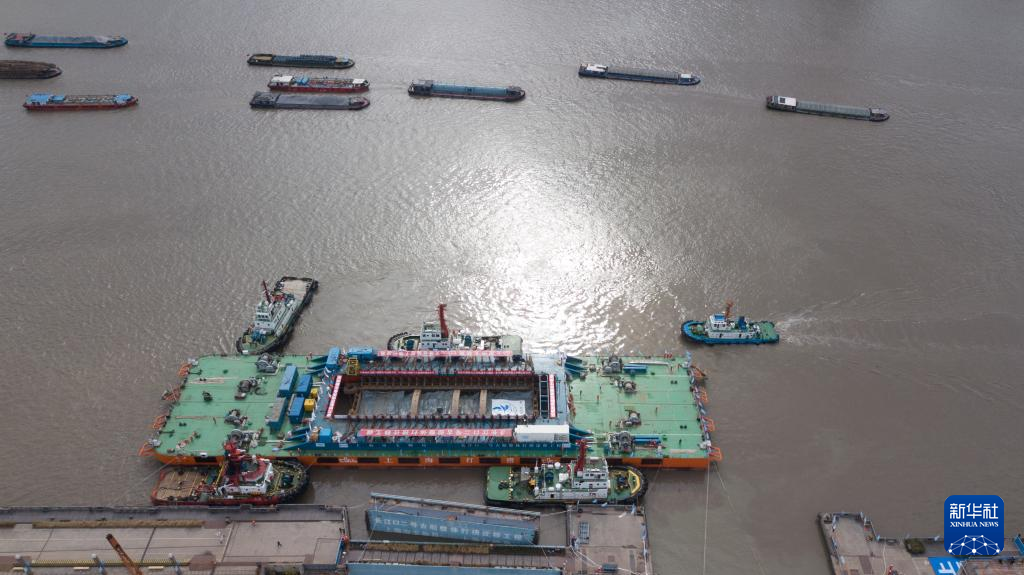

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
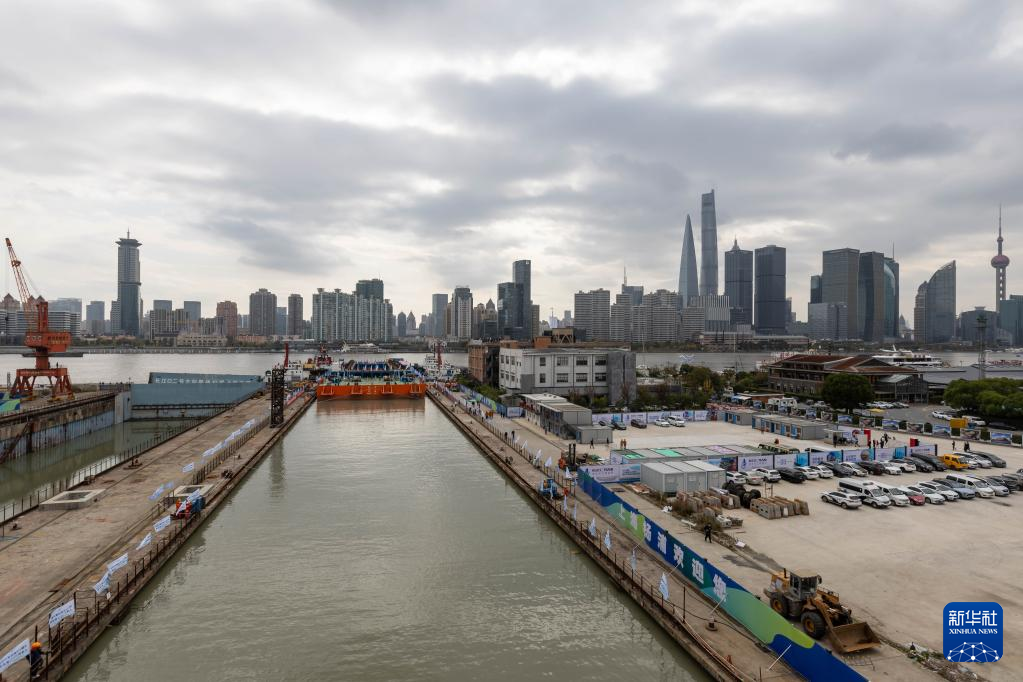

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Wang Xiang)
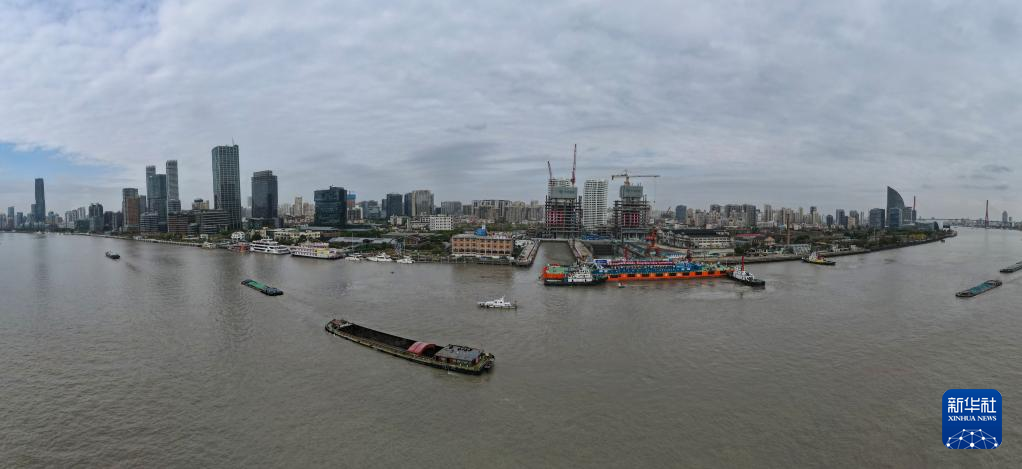

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)
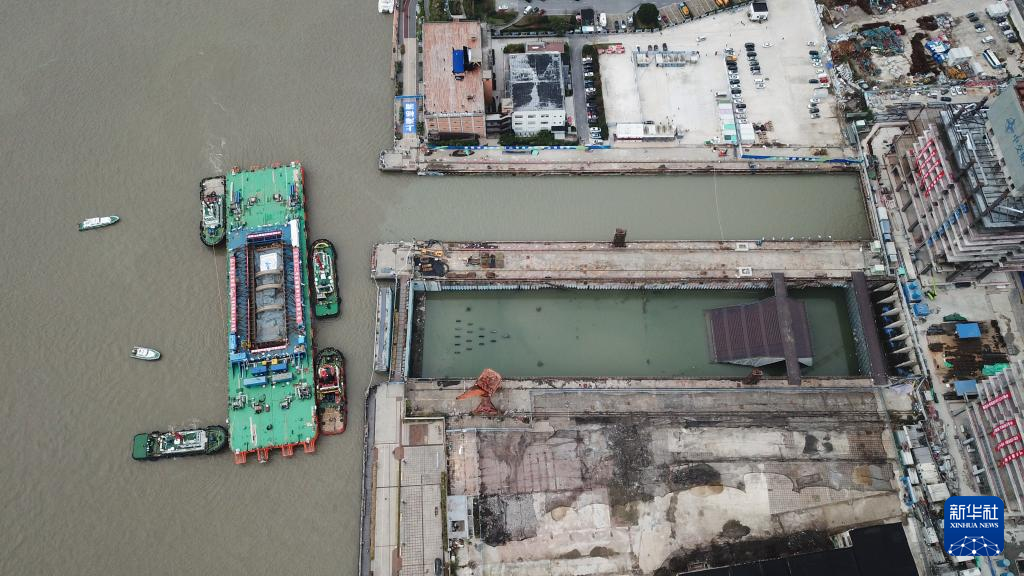

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
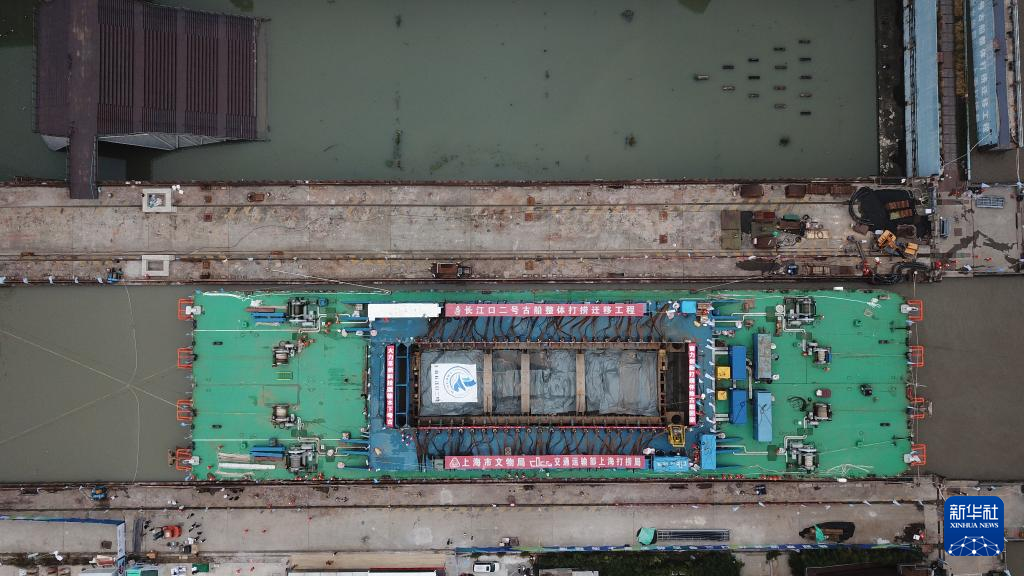
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
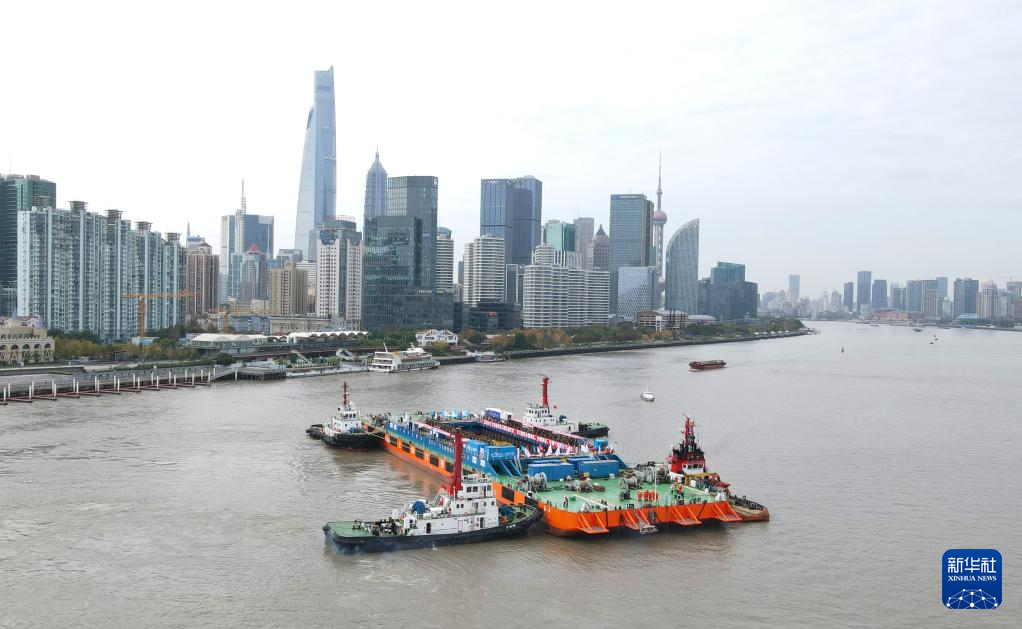

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)
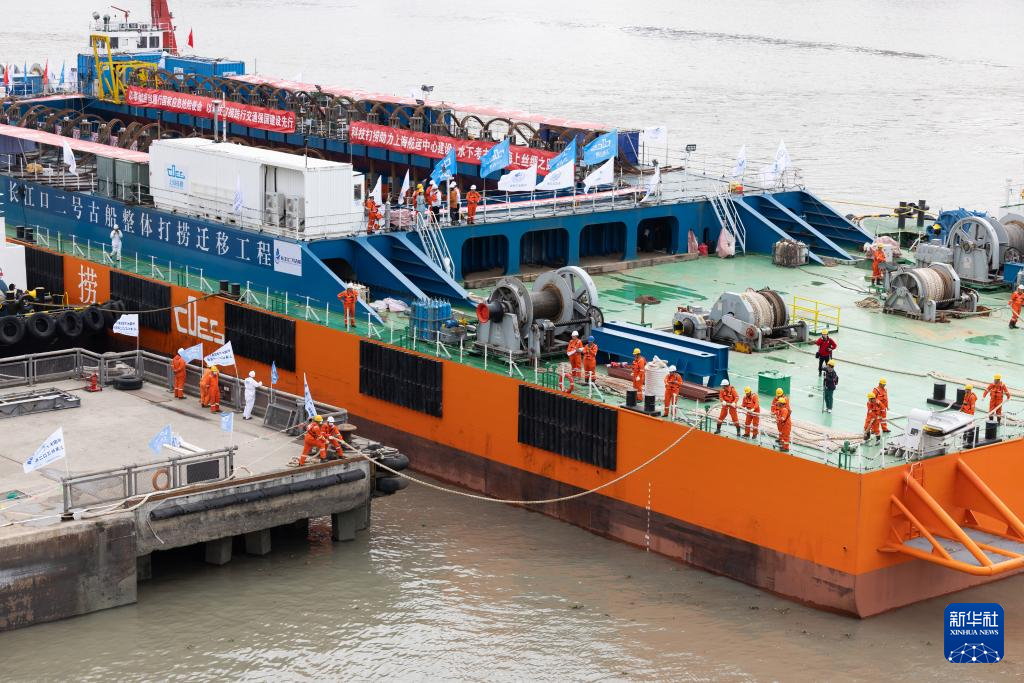

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Jin Liwang)
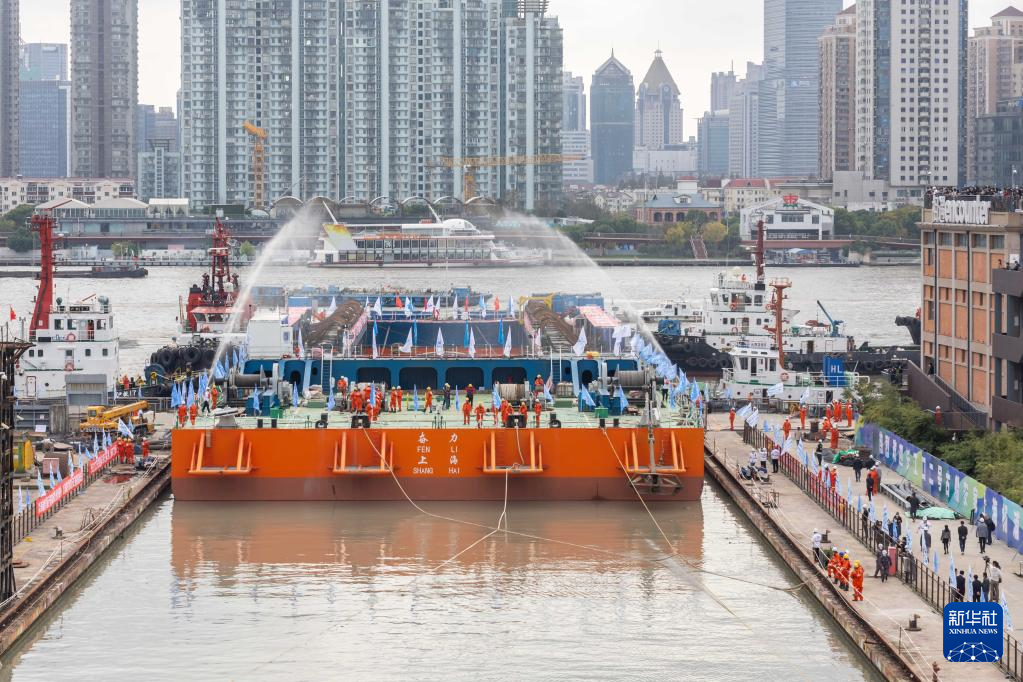

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Wang Xiang)
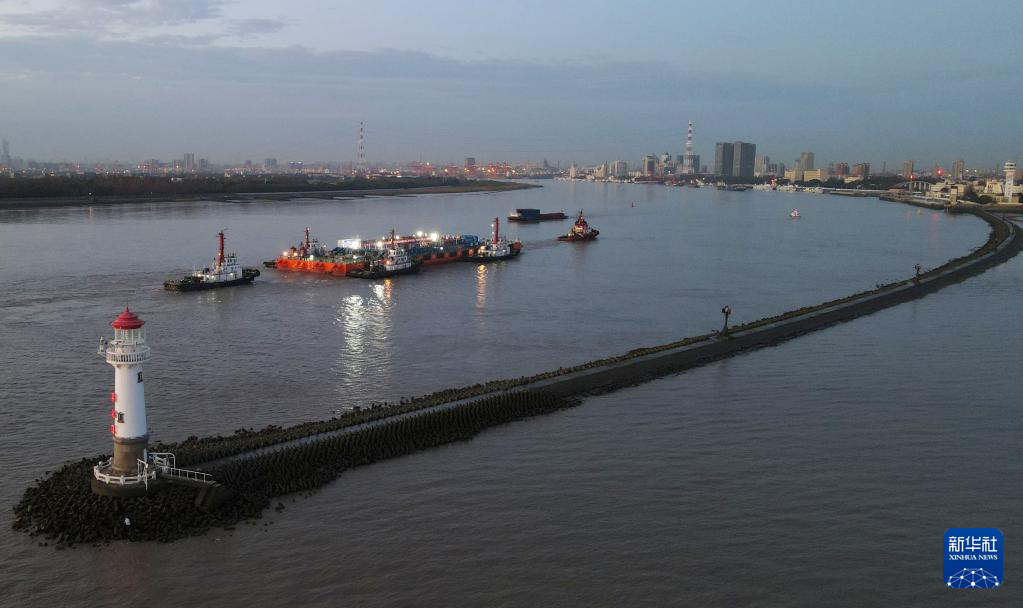

The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck is transferred to a dock near the Huangpu River in Shanghai, east China, Nov. 25, 2022.
The ancient shipwreck, one of the largest and best-preserved wooden shipwrecks discovered underwater in China to date, was lifted out of waters in Shanghai early Monday.
The Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck dates back to the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) of the Qing Dynasty. This salvage could offer a useful glimpse of shipbuilding technology during the Qing Dynasty. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)



